Terms
Vocab and terminology to have a good grasp of.
Moore's Law
The number of transistors on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years. This exponential rate of growth is what has been driving force behind the massive amounts of computing and technology development in recent years, with now inexpensive compute deployed at scale.
A integrated circuit (IC) or microchip or chip, is made of semiconductor material (silicon) with transistors in the silicon wired together.
Amdahl's Law
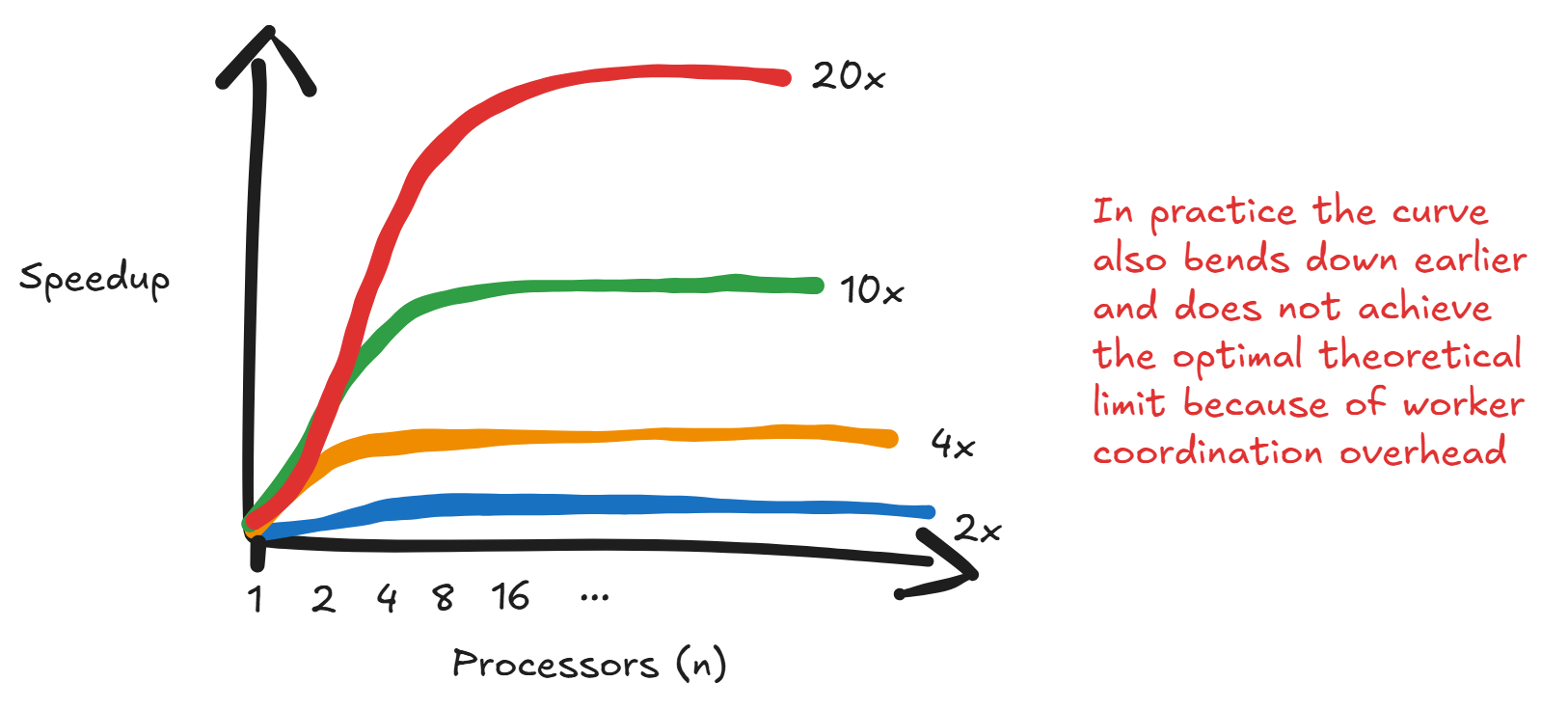
Amdahl's law states that the overall speedup of a task is limited by the portion of the task that cannot be parallelized. Even if you had infinite parallel processers, you are limited to the sequential part of the computation.
The law allows you to compute the speedup of a task given processors or workers:
Where is the fraction of the code that can be parallelized and is number of workers. You can think of it as time with 1 worker divided by time in non-parallelizable part added to the parallelized time . For a certain percentage of code that can be sped up, you are fundamentally capped to a theoretical speedup limit. As tends to infinity, you approach the asymptotic limit. If only 50% of the code is parallelizable, you can at most have a 2x speedup.
Monte-Carlo Simulation
Monte-Carlo methods use repeated random sampling to estimate the probability of a range of events occurring. For example, if you wanted to estimate the probability of getting 12 from a two dice roll, you simulate the dice rolling 10,000 times to get an accurate estimate. With predictive models you will have independent variables you generate random values for and dependent variables to be predicted based off those independent variables. You run simulations each time modifying the underlying params.
Likert Scale
Qualitative number scales e.g. "Rate X from 1 (bad) to 5 (good)".
Mainframe
Mainframes are large powerful computers built in the 1960s-1980s to handle large volumes of transactions and computations extremely reliably. They are built to run 24/7 without crashing.
I overheard an Amazon exec talk about how many companies are still using legacy mainframes because they work so well. He was using this as evidence on the point that many enterprises choose to stay with what works over adopting new flashy technologies, especially those touting AI transformations.
Thread Safety
Thread safe programs or code allows multiple threads to run without race conditions . This can also be applied to data types that are being used across multiple threads.
Amortized
Something being amortized meaning that the cost has been gradually written off over a period of time.
Example: "The price should be quite low because all the R&D has long since been amortized"
HPC Schedulers
In HPC a batch scheduler is used to divvy up resources and determine who gets what compute resources for how long. Generally you submit a request to the scheduler with info on the time, compute, and memory resources you need for your job.
Daemons
In software, a daemon pronounced DEE-MUN is a program that runs as a background process. By convention, a daemon process is named with d as a suffix, for example sshd or syslogd.
Underwriting
In real estate, underwriting is a detailed process by which a lender or investor assesses and mitigates risk before approving a loan or investment. It's a diligent process of evaluating a borrower's financial history, the property's condition, and potential for income. The goal is to determine the financial viability of a transaction and ensure the risk is acceptable to the underwriter. It's all about mitigating risk.
Hedging
In finance, hedging is to offset potential for loss by taking an opposing position or asset. If the main investment position suffers a large loss, then the hedge acts as insurance, and should provide gains that mitigates the adverse effects and exposure to the main position. The main purpose of hedging is to manage risk.
Shorting
Shorting a stock consists of borrowing shares from a broker, selling them, and then buying back the stock later to return to the lender, pocketing the difference if the price of the shares fall. A margin call can happen if the loss hits a maximum, in the which the lender will liquidate your assets unless you to deposit more funds to cover the position.
Shale Economics
Shale gas is a natural gas trapped in shale formations. It's an unconventional source as shale is distributed over larger areas in pockets. Shale gas is extracted through fracking - a process in which deep holes are drilled into shale rock followed by horizontal drilling to access more gas (shale reserves are typically horizontally distributed rather than vertically).
A shale revolution occurred in the US in which US crude oil production was boosted by exploitation of shale formations. This led to US becoming a world leading producer of natural gas, producing 20% of the world supply, 40% from shale. The economic feasibility of oil shale is debatable, as the production and processing costs are high due to the spotty and small nature of the projects and the specialist technology required. The economics is only viable when the cost of shale oil comes below the price of crude oil or other substitutes. As a result the last major investment into oil shale in the early 1980s incurred major losses, especially with collapses in oil prices.
Vaporware
Vaporware refers to software or hardware that has been advertised but is still in early development. It is commonly used to negatively connote products that are being prematurely promoted without yet being able to meet real world expectations.
The vaporware problem is common in high tech industry with entrepreneurs touting technology and products that are not mature yet and still have significant hurdles to overcome.
OEM, ODM, JDM Model
There are three major manufacturing models around bringing a product to market. The Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) model involves outsourcing the technical specifications of a design to the manufacturer, while retaining product design and IP. The Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) offloads most of the design work as well to the manufacturer - the tradeoff here is a faster product development and time to market, with the loss of design ownership and IP. The Joint Design Manufacturer (JDM) model, it is a hybrid of OEM and ODM where both outsourcing and manufacturing company cooperate closely on aspects of the design and manufacture of the product, allowing companies to retain ownership over critical design choices while also leveraging the manufacturing and technical abilities of their partner.
REST API
Representational State Transfer (REST) API refers to a software architectural style for building distributed systems (especially web services). It focuses on a stateless client-server model where resources are defined by unique URLs and interactions involve transferring representations of these resources (e.g. in JSONs or XML) between client and server. Implementing a REST API enables communication and data exchange between different software components over the internet using HTTP and resource based interaction.
Hence REST APIs provide a lightweight way to build web APIs and facilitate data exchange between apps, web services, and databases, or connect components in microservices architecture.
REST vs. RESTful API:
REST API is the architectural constraint, and a RESTful API or web service fully implements and adheres to those constraints.
Gross Margins
Gross Profit Margin is an important financial metric for profitability, and indicates the financial health of companies. It is the percentage of net revenue remaining after deducting the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Think of it as the profit the company makes for each dollar of revenue after paying for direct production costs.
Domain Specific Language (DSL)
A domain specific language is a programming language designed for a particular application domain and problem. Examples include SQL for database queries, HTML for web page structure, and CSS for web page styling. This is in contrast to general purpose languages (GPL) like Python.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Converting text in images into pure text. For example, you might want to OCR text from a screenshot into actual characters - this can be done with image-to-text GPTs.
Commoditization
An extremely important concept in business, commoditization is the process where goods or services become undifferentiated due to competition, leading to buyers only basing their purchases off of price. Commoditization of products and services occurs in crowded industries, and is a big threat to businesses by shrinking profit margins and decreasing customer loyalty.
Causes of commoditization:
- Technology diffusion - as technology spreads, competitors can easily duplicate product and features
- Information transparency - customers can easily compare prices and features, eroding brand differentiation
- Standardization - industry standards make products interchangeable (e.g. USB drives, airplane seats)
- Price competition - companies focusing mainly on price also nudges customers to value cost over uniqueness
Pareto Principle
The Pareto principle states that for many outcomes, 80% of the consequence come from 20% of the causes.
Mathematically, a large proportion of process variation comes from a small proportion of process variables.
In Pareto analysis, the problem solver identifies the top portion of causes that need to be addressed to resolve the majority of problems.
The Pareto principle can be used in day to day life to focus on what's actually important and ignore distractions. For instance if you get 100 emails a day, people naturally try to address all 100, when only 20 might be somewhat important, and 4 vital. If the remaining 80 are trivial and easy to answer people will give those attention first, resulting in distraction.
Be selective about what you put your resources and time into to get the best results for your effort.